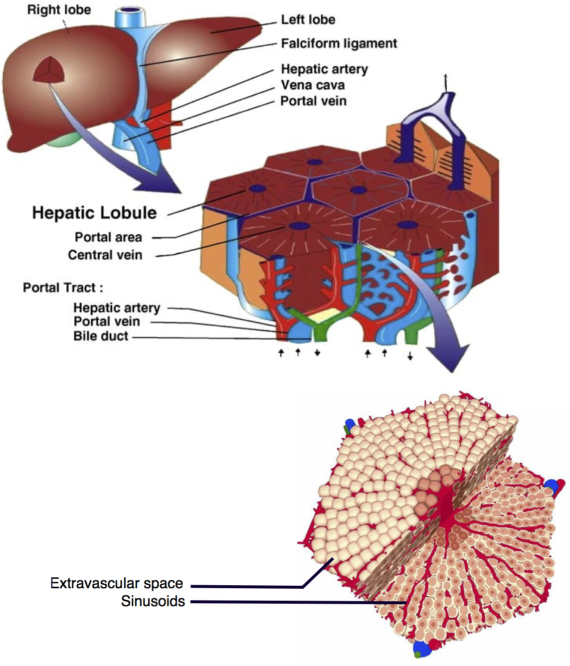
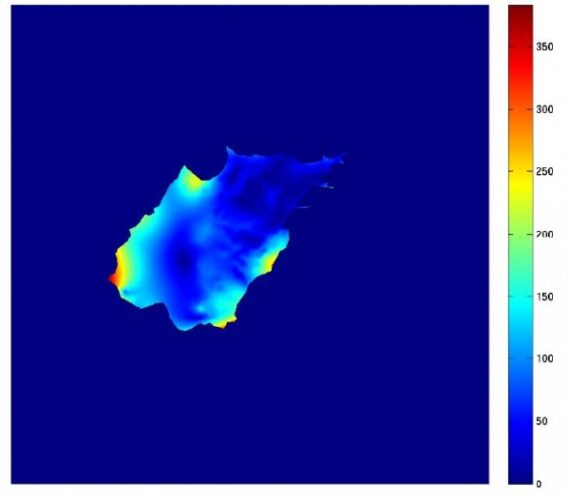
Modeling the perfusion characteristics of liver tissue may provide information useful in surgical treatment which require resection of the pathological tissue regions or for drug delivery. At the macro-scale the whole organ may be modeled as a porous medium with nonuniform, non isotropic permeability. At an intermediate scale, the tissue […]
Life Sciences
Many types of cell have the ability to migrate orchestrating in a complex way the poli/depolimerization of the actin network and actively generating a pattern of forces in the surrounding environment. Mathematics can be of support to understand such a complex phenomenon in two ways. Force traction microscopy is the determination of the stress […]
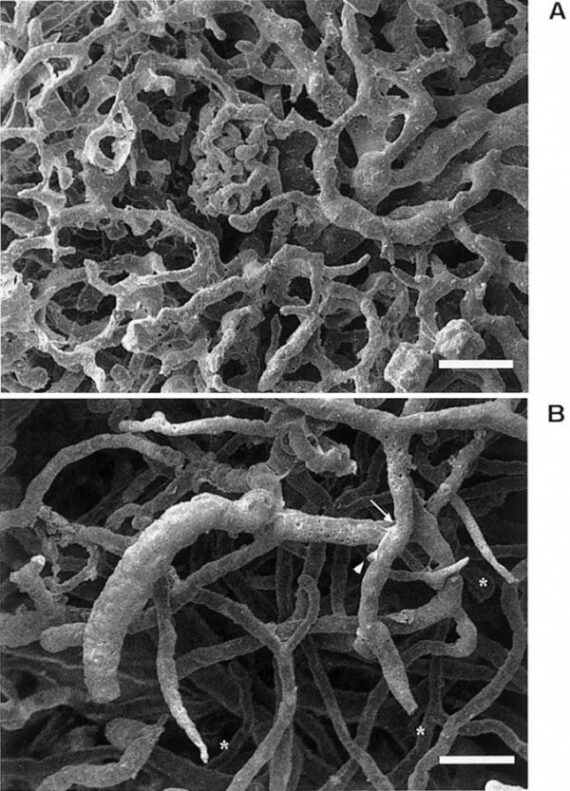
Blood circulation in capillaries occurs in a complex hierarchical network of capillaries. At this spatial scale the vessels deliver nutrients to the living tissues; tumor vessels characterized by a tortuous geometry, leaky walls and small transmural pressure gap are particularly ineffective in delivering drug to the malignant cells. Numerical simulations at a single […]
The study of cooperative migration and the onset of patterns in developing living organisms is an extremely multidisciplinary field of research, that combines biological information with the mathematical theories of nonlinear dynamics and the physics and mechanics of non-equilibrium processes. Cooperative migration and self-organization in living aggregates is known to […]
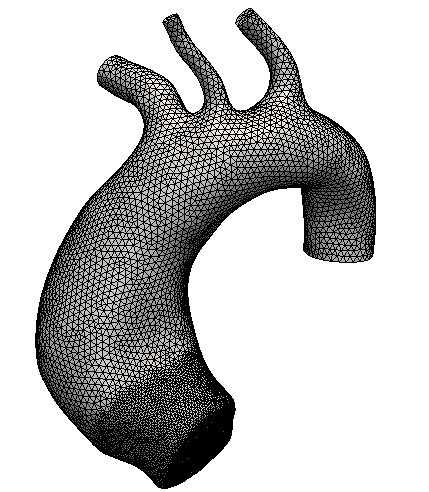
Once an anatomical model is constructed in the form of an implicit surface a mesh must be generated to perform the numerical simulations. For this reason we also develop a tool to generate suitable grids for CFD simulations. This step is critical since the mesh can change the accuracy of the numerical […]
Medical images are often affected by noise or artifacts. A MOX research topic concerns the reduction of metal artifacts (MAR) in X-ray computerized tomography (CT), and the development of techniques and procedures for the pre-processing of medical images. A second focus is the generation of automatic methods for the segmentation of different vessel district […]
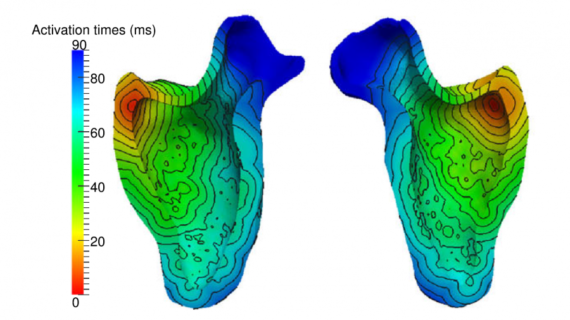
The cardiac insufficiency (CI) represents the main cause of hospitalization after the age of 65 years, and the related mortality is very high. There is nowadays a big interest in this pathology in order to find efficient therapies. In particular, a great attention has been done to the ventricular dissincrony (VD) […]
Nowadays ventricular assist devices (VAD) play an important role in the treatment of terminal heart failure. While the devices themselves have been widely studied there are no studies of patient-specific numerical simulation in this context. This could be explained by the fact that the presence of the device induces metallic artifacts and […]
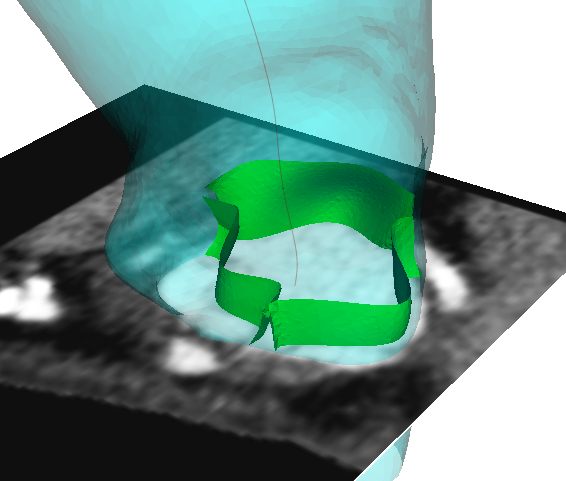
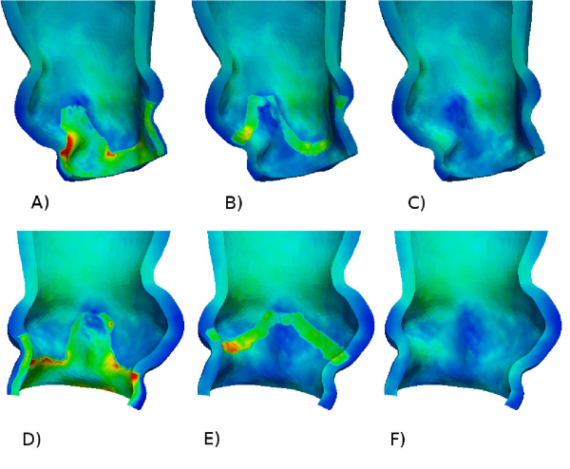
The presence of stent in aortic bioprostesis have been shown to increase stresses on the valve leaflets and to reduce dynamic root motion during the cardiac cycle. The research focused on the comparison of the forces developed in the aortic root after aortic valve replacement with stented or stentless bioprosthesis. To this aim fluid-structure […]
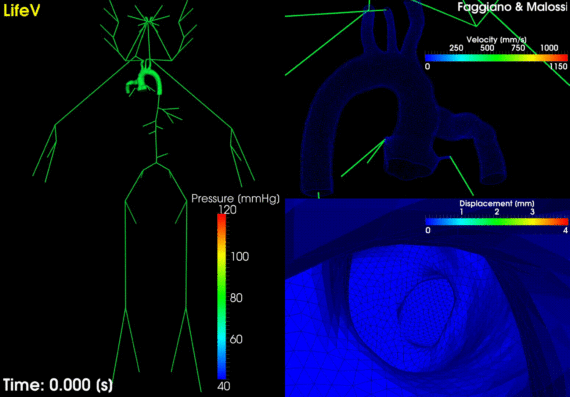
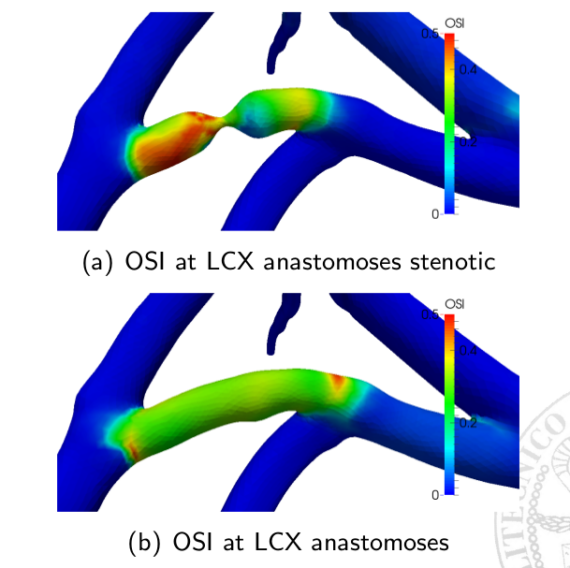
It is well known that Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) failure in the long term is mainly due to restenosis, which can be related to sub-optimal haemodynamical conditions near the grafts. Under this assumption, the research at MOX aims to a better understanding of CABG effects on coronary circulation and possibly to […]