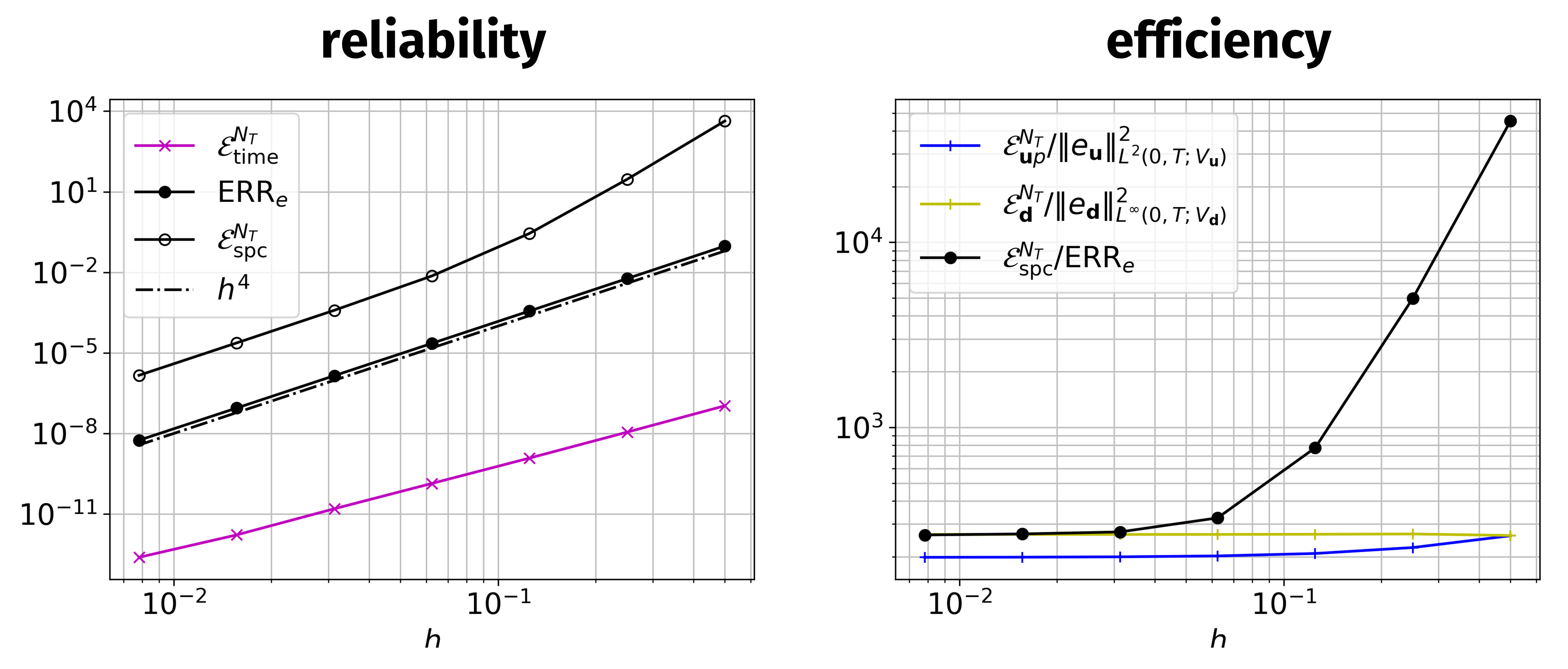
A new MOX Report entitled “A posteriori error analysis for a coupled Stokes-poroelastic system with multiple compartments” by Fumagalli, I.; Parolini, N.; Verani, M. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/50-2024.pdf Abstract: The computational effort entailed in the discretization of fluid-poromechanics systems is typically highly demanding. This is particularly true for models of multiphysics flows in the brain, due to the geometrical complexity of the cerebral anatomy – requiring a very fine computational mesh for finite element discretization – and to the high number of variables involved. Indeed, this kind of problems can be modeled by a coupled system encompassing the Stokes equations for the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain ventricles and Multiple-network Poro-Elasticity (MPE) equations describing the brain tissue, the interstitial fluid, and the blood vascular networks at different space scales. The present work aims to rigorously derive a-posteriori error estimates for the coupled Stokes-MPE problem, as a first step towards the design of adaptive refinement strategies or reduced order models to decrease the computational demand of the problem. Through numerica! l experim ents, we verify the reliability and optimal efficiency of the proposed a-posteriori estimator and identify the role of the different solution variables in its composition.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “A comparative analysis of mesh-based and particle-based numerical methods for landslide run-out simulations” by Fois, M.; Gatti, […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Uncovering mortality patterns and hospital effects in COVID-19 heart failure patients: a novel Multilevel logistic cluster-weighted modeling […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Personalized pressure conditions and calibration for a predictive computational model of coronary and myocardial blood flow” by […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Assessing the Impact of Hybrid Teaching on Students’ Academic Performance via Multilevel Propensity Score-based techniques” by Ragni, […]