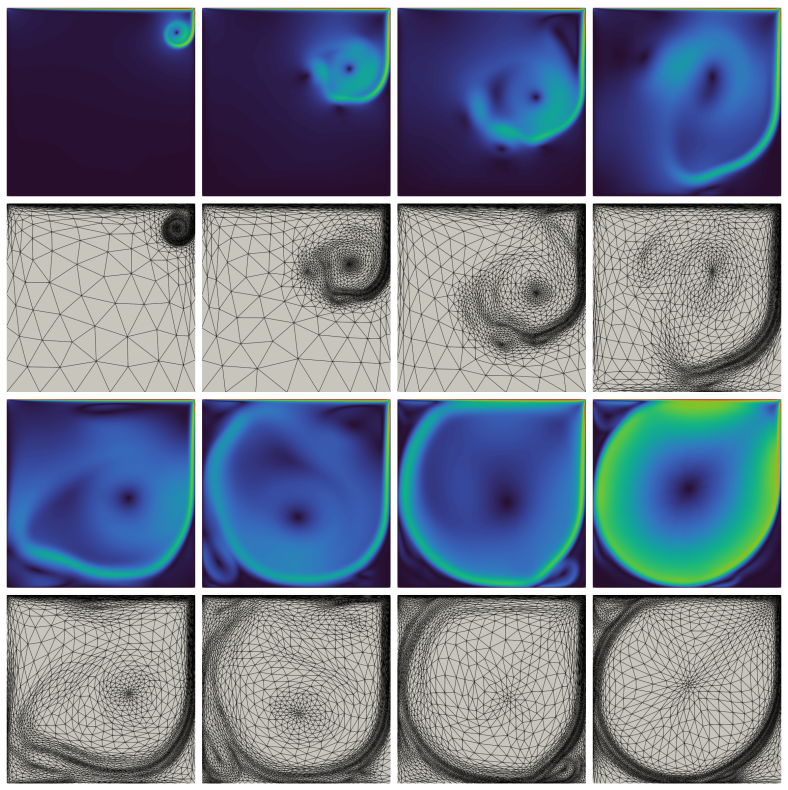
A new MOX Report entitled “Space – time mesh adaptation for the VMS – Smagorinsky modeling of high Reynolds number flows ” by Temellini, E.; Ferro, N.; Stabile, G.; Delgado Avila, E.; Chacon Rebollo, T.; Perotto, S. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/60-2024.pdf Abstract: Traditional methods, such as Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations and Large Eddy Simulations (LES), provide consolidated tools for the numerical approximation of high Reynolds number flows in a wide range of applications – from green energy to industrial design. In general, RANS modeling is practical when the main interest is the time-averaged flow behavior. LES equations offer detailed insights into flow dynamics and a more accurate solution, but the high computational demand necessitates innovative strategies to reduce costs while maintaining precision. In this study, we enhance the Variational MultiScale (VMS)-Smagorinsky LES model by relying on an adaptive discretization strategy in both space and time, driven by a recovery-based a posteriori error analysis. We assess the effectiveness of the approach in capturing flow characteristics across a wide range of Reynolds numbers through benchmark tests.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “Functional principal component analysis for incomplete space-time data” by Palummo, A.;, Arnone, E.; Formaggia, L.; Sangalli, L.M. […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A mixed-dimensional formulation for the simulation of slender structures immersed in an incompressible flow” by Lespagnol, F.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Causal effect of chemotherapy received dose intensity on survival outcome: a retrospective study in osteosarcoma” by Spreafico, […]
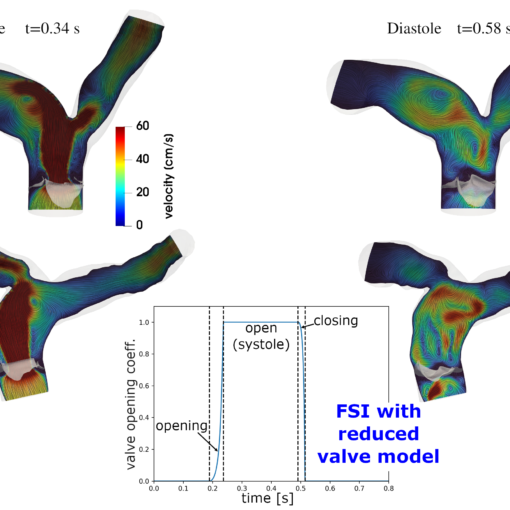
A new MOX Report entitled “Computational haemodynamics for pulmonary valve replacement by means of a reduced Fluid-Structure Interaction model” by Criseo, M.; […]