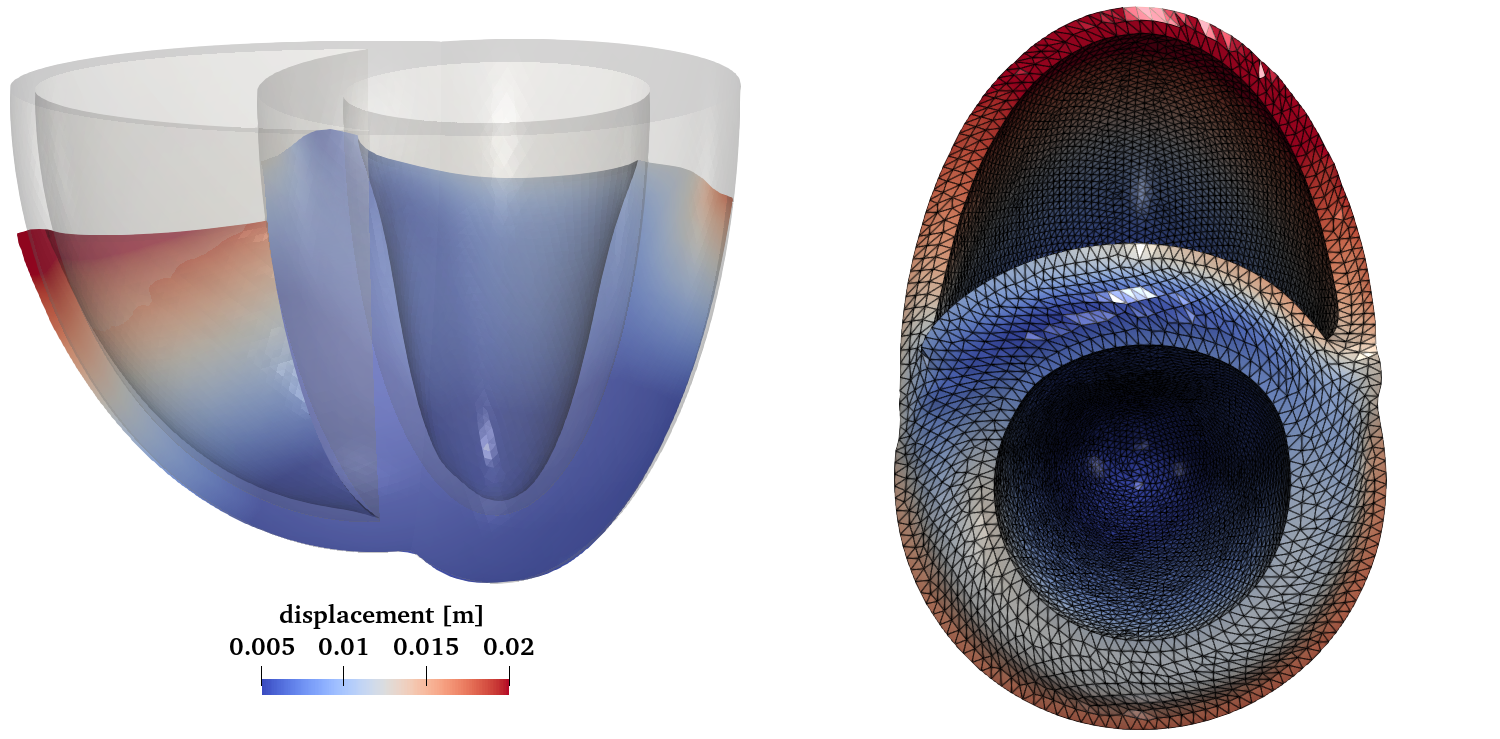
A new MOX Report entitled “A software benchmark for cardiac elastodynamics” by Arostica, R.; Nolte, D.; Brown, A.; Gebauer, A.; Karabelas, E.; Jilberto, J.; Salvador, M.; Bucelli, M.; Piersanti, R.; Osouli, K.; Augustin, C.; Finsberg, H.; Shi, L.; Hirschvogel, M.; Pfaller, M.; Africa, P.C.; Gsell, M.; Marsden, A.; Nordsletten, D.; Regazzoni, F.; Plank, G.; Sundnes, J.; Dede’, L.; Peirlinck, M.; Vedula, V.; Wall, W.; Bertoglio, C. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/108-2024.pdf Abstract: In cardiovascular mechanics, reaching consensus in simulation results within a physiologically relevant range of parameters is essential for reproducibility purposes. Although currently available benchmarks contain some of the features that cardiac mechanics models typically include, some important modeling aspects are missing. Therefore, we propose a new set of cardiac benchmark problems and solutions for assessing passive and active material behaviour, viscous effects, and pericardial boundary condition. The problems proposed include simplified analytical fiber definitions and active stress models on a monoventricular and biventricular domains, allowing straightforward testing and validation with already developed solvers.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “Multi-state Modeling of Delay Evolution in Suburban Rail Transports” by Colombo, S.; Gimenez Zapiola, A.; Ieva, F.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Nonlinear morphoelastic theory of biological shallow shells with initial stress” by Andrini, D.; Magri, M.; Ciarletta, P. […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A topology optimization framework for scaffold design in soilless cultivation” by Speroni, G.; Mondini, N.; Ferro, N.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “lifex-ep: a robust and efficient software for cardiac electrophysiology simulations” by Afriaca, P.C.A; Piersanti, R.; Regazzoni, F.; […]