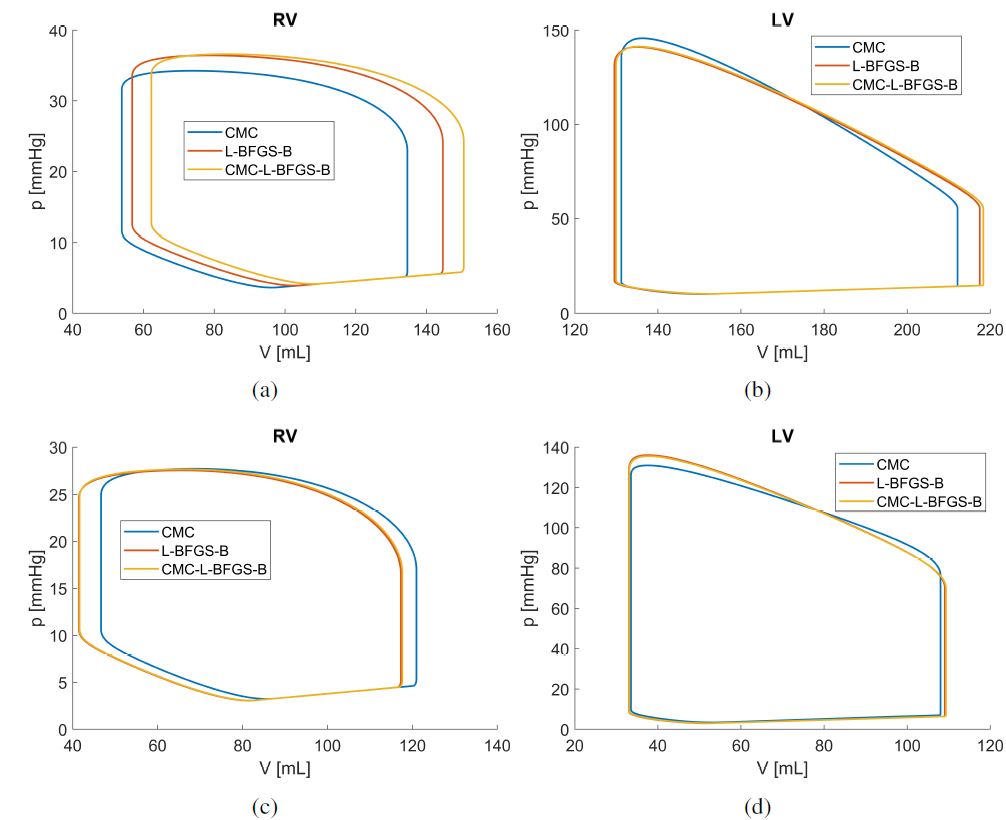
A new MOX Report entitled “Two new calibration techniques of lumped-parameter mathematical models for the cardiovascular system” by Tonini, A., Regazzoni, F., Salvador, M., Dede’, L., Scrofani, R., Fusini, L., Cogliati, C., Pontone, G., Vergara, C., Quarteroni, A. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/38-2024.pdf Abstract: Cardiocirculatory mathematical models serve as valuable tools for investigating physiological and pathological conditions of the circulatory system. To investigate the clinical condition of an individual, cardiocirculatory models need to be personalized by means of calibration methods. In this study we propose a new calibration method for a lumped-parameter cardiocirculatory model. This calibration method utilizes the correlation matrix between parameters and model outputs to calibrate the latter according to data. We test this calibration method and its combination with L-BFGS-B (Limited memory Broyden – Fletcher – Goldfarb – Shanno with Bound constraints) comparing them with the performances of L-BFGS-B alone. We show that the correlation matrix calibration method and the combined one effectively reduce the loss function of the associated optimization problem. In the case of in silico generated data, we show that the two new calibration methods are robust with respect to the initial guess of parameters and to the presence of noise in the data. Notably, the correlation matrix calibration method achieves the best results in estimating the parameters in the case of noisy data and it is faster than the combined calibration method and L-BFGS-B. Finally, we present real test case where the two new calibration methods yield results comparable to those obtained using L-BFGS-B in terms of minimizing the loss function and estimating the clinical data. This highlights the effectiveness of the new calibration methods for clinical applications.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “Polytopal discontinuous Galerkin methods for low-frequency poroelasticity coupled to unsteady Stokes flow” by Botti, M.; Fumagalli, I.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “An interpretable and transferable model for shallow landslides detachment combining spatial Poisson point processes and generalized additive […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A geometry aware arbitrary order collocation Boundary Element Method solver for the potential flow past three dimensional […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Noise-Adaptive Conformal Classification with Marginal Coverage” by Bortolotti, T.; Wang, Y. X. R.; Tong, X.; Menafoglio, A.; […]