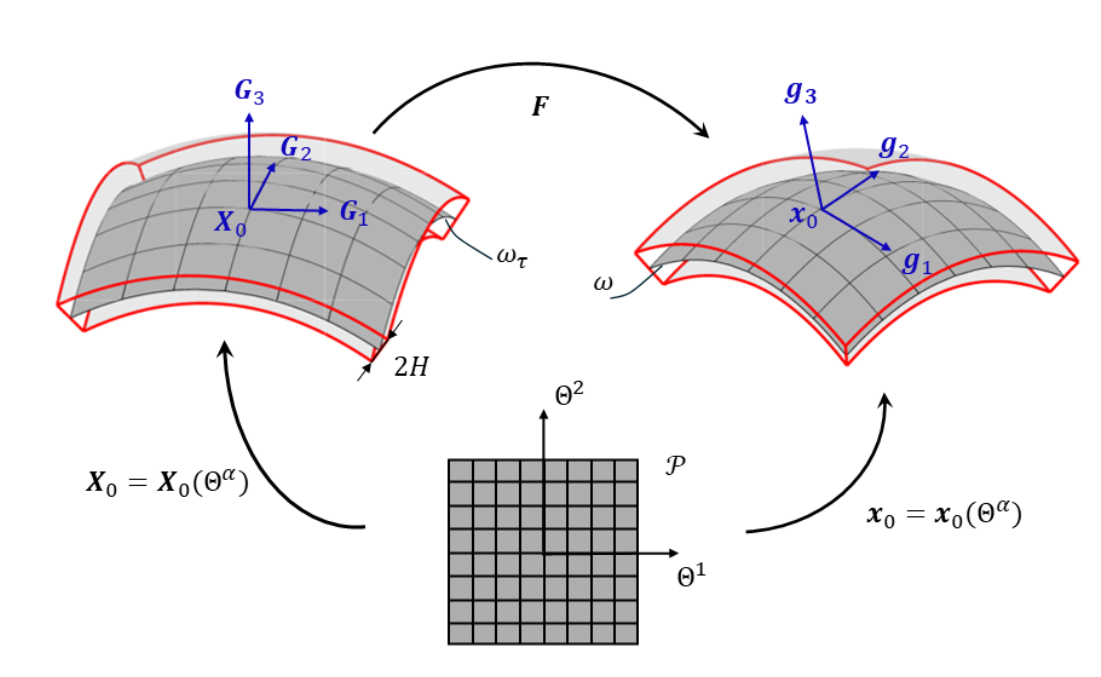
A new MOX Report entitled “Nonlinear morphoelastic theory of biological shallow shells with initial stress” by Andrini, D.; Magri, M.; Ciarletta, P. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/04-2025.pdf Abstract: Shallow shells are widely encountered in biological structures, especially during embryogenesis, when they undergo significant shape variations. As a consequence of geometric frustration caused by underlying biological processes of growth and remodeling, such thin and moderately curved biological structures experience initial stress even in the absence of an imposed deformation. In this work, we perform a rigorous asymptotic expansion from three-dimensional elasticitiy to obtain a nonlinear morphoelastic theory for shallow shells accounting for both initial stress and large displacements. By application of the principle of stationary energy for admissible variation of the tangent and normal displacement fields with respect to the reference middle surface, we derive two generalised nonlinear equilibrium equations of the Marguerre-von K´arm´an type. We illustrate how initial stress distributions drive the emergence of spontaneous mean and Gaussian curvatures which are generally not compatible with the existence of a stress free configuration. We also show how such spontaneous curvatures influence the structural behavior in the solutions of two systems: a saddle-like and a cylindrical shallow shell.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “On the Impact of Light Spectrum on Lettuce Biophysics: A Dynamic Growth Model for Vertical Farming” by […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Efficient particle generation for depth-averaged and fully 3D MPM using TIFF image data” by Fois, M.; de […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A novel metric – based mesh adaptation algorithm for 3D periodic domains” by Speroni, G.; Ferro, N. […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Influence of patient-specific acute myocardial ischemia maps on arrhythmogenesis: a computational study” by Corda, A.; Pagani, S.; […]