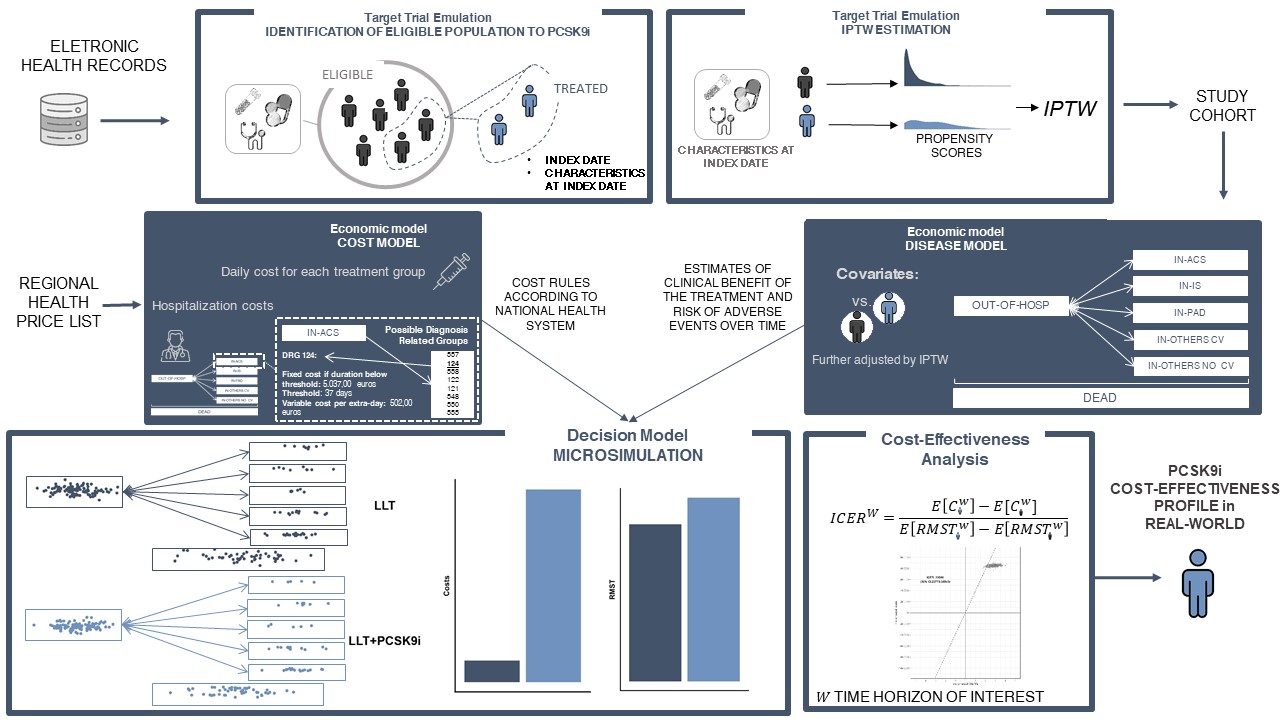
A new MOX Report entitled “Flexible approaches based on multi-state models and microsimulation to perform real-world cost-effectiveness analyses: an application to PCSK9-inhibitors ” by Gregorio, C.; Rea, F.; Ieva, F.; Scagnetto, A.; Indennidade, C.; Cappelletto, C.; Di Lenarda, A.; Barbati, G. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/30-2024.pdf Abstract: Objectives: This study aims to show the application of flexible statistical methods in real-world cost-effectiveness analyses applied in the cardiovascular field, focusing specifically on the use of PCSK9 inhibitors for hyperlipidaemia. Methods: The proposed method allowed us to use an electronic health database to emulate a target trial for cost-effectiveness analysis using multi-state modelling and microsimulation. We formally established the study design and provided precise definitions of the causal measures of interest, while also outlining the assumptions necessary for accurately estimating these measures using the available data. Additionally, we thoroughly considered goodness-of-fit assessments and sensitivity analyses of the decision model, which are crucial to capture the complexity of individuals’ healthcare pathway and to enhance the validity of this type of health economic models. Results: In the disease model, the Markov assumption was found to be inadequate, and a “time-reset” timescale was implemented together with the use of a time-dependent variable to incorporate past hospitalization history. Furthermore, the microsimulation decision model demonstrated a satisfying goodness-of-fit, as evidenced by the consistent results obtained in the short-term horizon compared to a non-model-based approach. Notably, only in the long-term follow-up PCSK9 inhibitors revealed their favourable cost-effectiveness, with a minimum willingness-to-pay of 39,000 Euro/LY gained. Conclusions: The approach demonstrated its significant utility in several ways. Unlike non-model based or alternative model-based methods, it enabled to 1) investigate long-term cost-effectiveness comprehensively, 2) employ an appropriate disease model that aligns with the specific problem under study, and 3) conduct subgroup-specific cost-effectiveness analyses to gain more targeted insights.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “Adaptive digital twins for predictive decision-making: Online Bayesian learning of transition dynamics” by Varetti, E.; Torzoni, M.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A scalable well-balanced numerical scheme for a depth-integrated lava flow model” by Gatti, F.; de Falco, C.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Analytical interpretation of hemodynamic data in patients with intracardiac shunts: role of mathematical modeling” by Paolo, F.; […]
A new MOX Report entitled “Clinical and Genomic-Based Decision Support System to Define the Optimal Timing of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in […]