A new MOX Report entitled “Exploring nitrogen dioxide spatial concentration via physics-informed multiple quantile regression” by De Sanctis, M.F.; Di Battista, I.; Arnone, E.; Castiglione, C.; Palummo, A.; Bernardi, M.; Ieva, F.; Sangalli, L.M. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection.
Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/32-2025.pdf
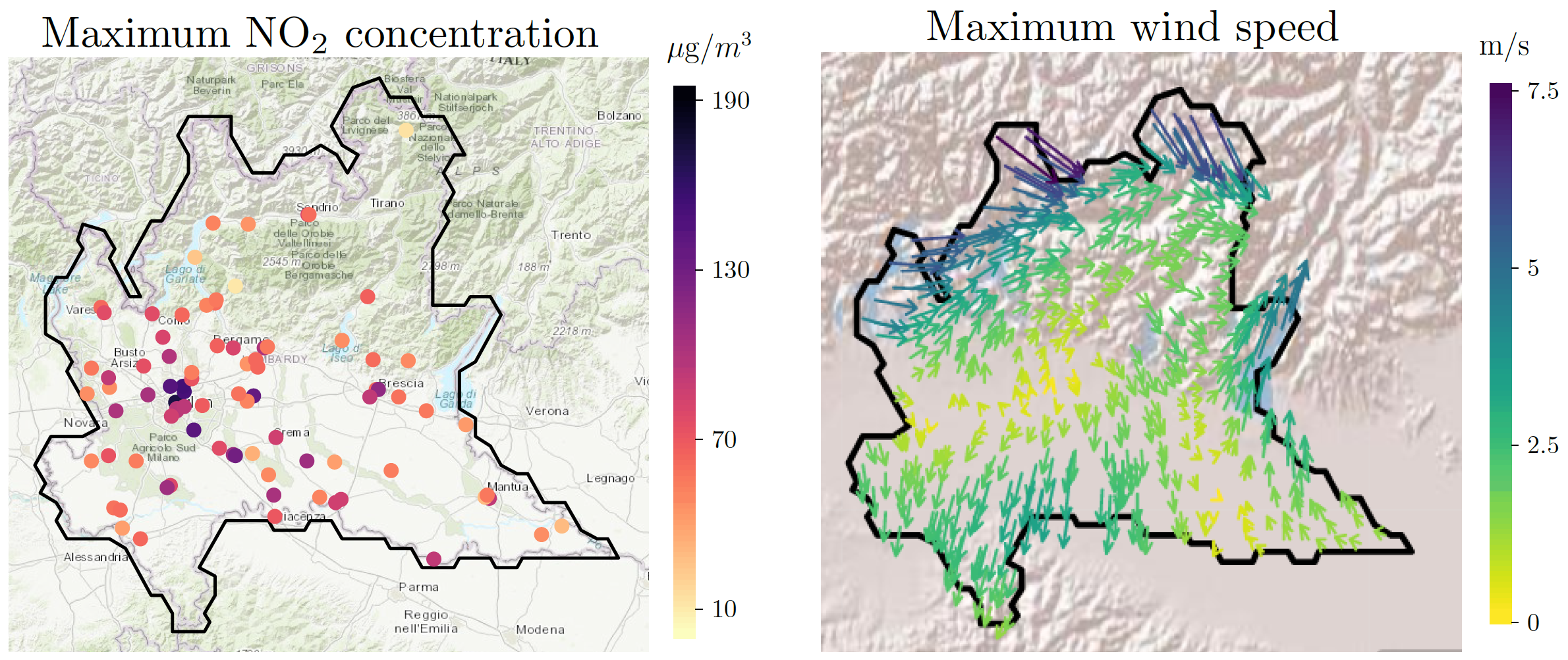
Abstract: Understanding the spatial distribution of air pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), is crucial for assessing environmental and health impacts, particularly in densely populated and industrialized regions. This paper introduces a novel method for estimating multiple spatial quantiles, ensuring the monotonicity of the resulting estimates. The proposed model builds upon recent advancements in quantile regression, and incorporates physical information of the phenomenon under analysis, to address the challenges posed by anisotropy, non-stationarity and skewness, typically observed in environmental data. For instance, in the study of air pollutants concentration, the model permits the inclusion of information concerning air-circulation, and in particular the physics of wind streams, which strongly influences the pollutant concentration. Moreover, the monotone estimation of the quantile maps yields a fully nonparametric reconstruction of ! the pollu tant probability density function, at any spatial location. This in turn enables the construction of probability maps, that quantify the likelihood of exceeding regulatory thresholds set by policymakers, offering valuable information for environmental monitoring policies, aimed at mitigating the adverse effects of air pollution.