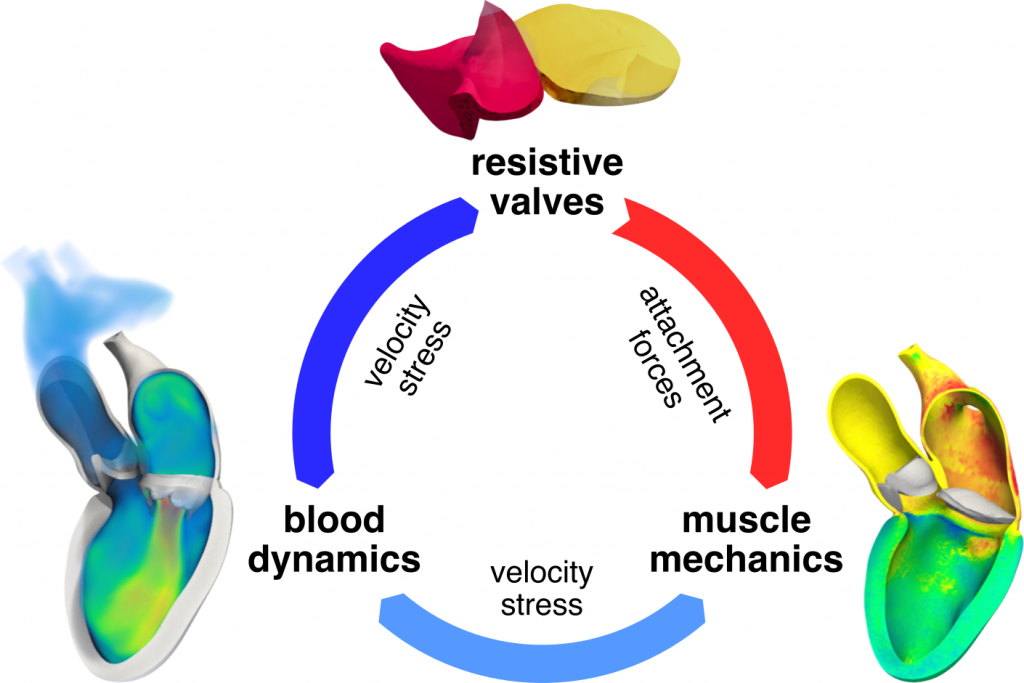
A new MOX Report entitled “Coupling models of resistive valves to muscle mechanics in cardiac fluid-structure interaction simulations” by Bucelli, M.; Dede’, L. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection.
Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/34-2025.pdf
Abstract: To accurately simulate all phases of the cardiac cycle, computational models of hemodynamics in heart chambers need to include a sufficiently faithful model of cardiac valves. This can be achieved efficiently through resistive methods, and the resistive immersed implicit surface (RIIS) model in particular [Fedele et al., BMMB, 2017]. However, the conventional RIIS model is not suited to fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulations, since it neglects the reaction forces by which valves are attached to the cardiac walls, leading to models that are not consistent with Newton’s laws. In this paper, we propose an improvement to RIIS to overcome this limitation, by adding distributed forces acting on the structure to model the attachment of valves to the cardiac walls. The modification has a minimal computational overhead thanks to an explicit numerical discretization scheme. Numerical experiments in both idealized and realistic settings demo! nstrate t he effectiveness of the proposed modification in ensuring the physical consistency of the model, thus allowing to apply RIIS and other resistive valve models in the context of FSI simulations.