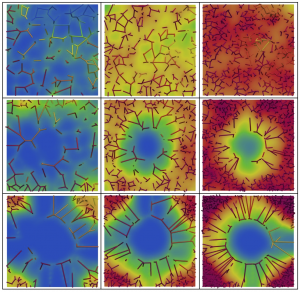
A new MOX Report entitled ” Modeling Hypoxia Induced Radiation Resistance and the Impact of Radiation Sources ” by Possenti, L.; Vitullo, P.; Cicchetti, A.; Zunino, P.; Rancati, T. has appeared in the MOX Report Collection. Check it out here: https://www.mate.polimi.it/biblioteca/add/qmox/65-2024.pdf Abstract: Hypoxia contributes significantly to resistance in radiotherapy. Our research rigorously examines the influence of microvascular morphology on radiotherapy outcome, specifically focusing on how microvasculature shapes hypoxia within the microenvironment and affects resistance to a standard treatment regimen (30 X 2 Gy). Our computational modeling extends to the effects of different radiation sources. For photons and protons, our analysis establishes a clear correlation between hypoxic volume distribution and treatment effectiveness, with vascular density and regularity playing a crucial role in treatment success. On the contrary, carbon ions exhibit distinct effectiveness, even in areas of intense hypoxia and poor vascularization. This finding points to the potential of carbon-based hadron therapy in overcoming hypoxia-induced resistance to RT. Considering that the spatial scale analyzed in this study is closely aligned with that of imaging data voxels, we also address the implications of these findings in a clinical context envisioning the possibility of detecting subvoxel hypoxia.
You may also like
A new MOX Report entitled “Fully-Mixed Virtual Element Method for the Biot Problem” by Botti, M.; Prada, D.; Scotti, A.; Visinoni, M. […]
A new MOX Report entitled “A gentle introduction to interpolation on the Grassmann manifold” by Ciaramella, G.; Gander, M.J.; Vanzan, T. has […]
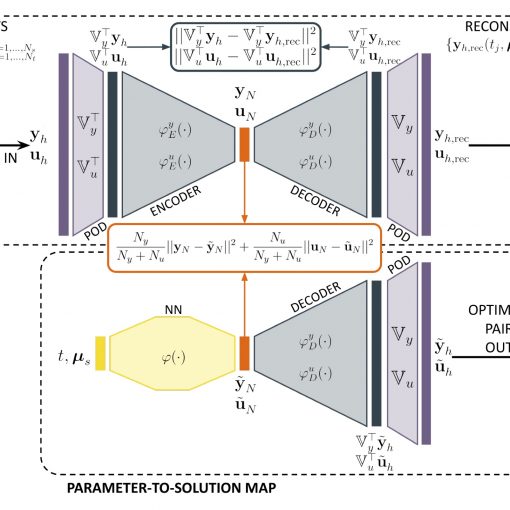
A new MOX Report entitled “Real-time optimal control of high-dimensional parametrized systems by deep-learning based reduced order models” by Tomasetto, M.; Manzoni, […]
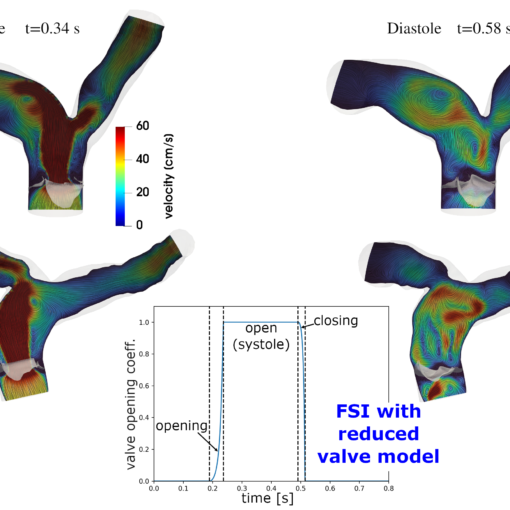
A new MOX Report entitled “Computational haemodynamics for pulmonary valve replacement by means of a reduced Fluid-Structure Interaction model” by Criseo, M.; […]